Understanding Blockchain Finance: Innovations and Impacts on
- By 苹果im冷钱包
- 2025-04-14 00:20:45
Introduction to Blockchain Finance
In recent years, the term blockchain has surged in popularity, particularly in relation to finance. While many individuals may associate blockchain with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, its applications extend far beyond digital currencies. Blockchain technology offers a decentralized ledger system that is secure, transparent, and immutable—capabilities that are transforming the financial landscape. The advent of blockchain in finance has led to innovations that are reshaping traditional banking practices, reducing costs, and enhancing security.
This article delves into the intricate relationship between blockchain and finance, examining how this revolutionary technology is influencing modern banking systems, investment strategies, and the overall economy. We will explore the various components of blockchain finance, its challenges, potential benefits, and future prospects.
What is Blockchain Finance?
Blockchain finance refers to the application of blockchain technology within the financial sector. This encompasses a variety of use cases, including but not limited to digital currencies, smart contracts, decentralized finance (DeFi), and supply chain financing. At its core, blockchain finance utilizes a distributed ledger to facilitate and record transactions in a secure and transparent manner.
One of the foundational aspects of blockchain technology is its decentralized nature. Unlike traditional financial systems that rely on centralized entities such as banks to verify and process transactions, blockchain operates through a network of nodes. Each participant in the network has access to the entire ledger, thus eliminating the need for intermediaries. This decentralization is key to enhancing security and reducing the potential for fraud.
Key Components of Blockchain Finance
Blockchain finance is built upon several key components that collectively contribute to its unique advantages:
- Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT): The backbone of blockchain finance, DLT allows for the secure and transparent recording of transactions across a network of computers.
- Smart Contracts: These are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. Smart contracts automate processes and reduce the need for manual intervention.
- Cryptocurrencies: Digital currencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum play a pivotal role in blockchain finance by enabling peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): DeFi encompasses a range of financial services—including lending, borrowing, and trading—conducted on blockchain platforms without traditional banks.
- Tokenization: This involves converting real-world assets into digital tokens that can be traded on blockchain networks, enhancing liquidity and accessibility.
The Advantages of Blockchain in Finance
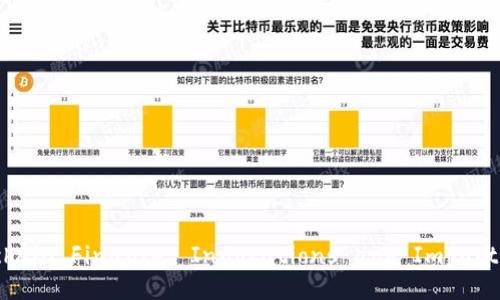
The integration of blockchain technology into financial systems brings numerous advantages:
- Enhanced Security: Transactions recorded on a blockchain are cryptographically secured, making it nearly impossible for malicious actors to alter transaction data.
- Lower Costs: By eliminating intermediaries, blockchain finance reduces transaction fees and operational costs for businesses and consumers.
- Increased Transparency: Blockchain's immutable ledger allows all participants to view the same information in real-time, fostering trust and accountability.
- Faster Transactions: Blockchain enables near-instant settlements as transactions do not require traditional banking hours or processes.
- Financial Inclusion: Blockchain technology offers access to financial services for unbanked and underbanked populations, promoting greater economic equality.
Challenges in Blockchain Finance
Despite its numerous advantages, blockchain finance faces several challenges that could hinder widespread adoption:
- Regulatory Uncertainty: As a relatively new technology, blockchain finance operates within a complex regulatory environment that varies significantly across jurisdictions.
- Scalability Issues: Many blockchain networks struggle with scalability, particularly during periods of high demand, which can lead to slower transaction speeds and increased costs.
- Security Concerns: While blockchain itself is secure, other components, such as wallets and exchanges, may be vulnerable to attacks, leading to potential loss of funds.
- Interoperability: The lack of standardization among different blockchain networks can create challenges when trying to integrate various platforms and systems.
- User Experience: The technical complexity of blockchain-based systems may deter everyday users, highlighting the need for user-friendly interfaces and solutions.
Future of Blockchain Finance
The future of blockchain finance is promising, with continual innovations emerging within the space. The increasing popularity of DeFi platforms indicates a shift towards more decentralized financial practices. As more users become aware of these alternatives, traditional banking institutions may need to adapt and innovate to remain competitive.
Moreover, regulatory bodies are beginning to provide clearer guidelines, which could facilitate greater adoption of blockchain solutions within mainstream finance. Enhanced collaboration between startups, established financial institutions, and regulators is likely to accelerate the development of innovative financial products that leverage blockchain technology. In addition, advancements in technology aimed at addressing scalability and interoperability challenges will further enhance the viability of blockchain finance.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How does blockchain technology differ from traditional banking systems?
Blockchain technology significantly differs from traditional banking systems in several ways. Primarily, blockchain operates on a decentralized model, meaning that it does not rely on central authorities or intermediaries, such as banks, to facilitate transactions. Transactions are processed and verified by a network of nodes, ensuring a level of transparency and security that is often lacking in traditional banking.
In addition, blockchain systems provide enhanced security through cryptographic techniques that secure transaction data. Traditional banking systems, conversely, are vulnerable to data breaches and fraud because they maintain central points of failure. Furthermore, transactions on blockchain can be executed in real-time and at a lower cost, while traditional banking often involves delays due to processing times and high fees associated with third-party intermediaries.
Overall, the key difference lies in the structure and approach each system employs to process and secure transactions, with blockchain offering a more transparent and efficient alternative.
2. What are the potential risks associated with using blockchain in finance?
While blockchain presents many opportunities within finance, several risks must be considered. One significant risk is regulatory uncertainty. With blockchain technology evolving rapidly, regulators globally are still determining how to approach this new paradigm. The absence of clear guidelines can create an unpredictable environment for businesses looking to implement blockchain solutions.
Another risk involves security vulnerabilities. Although blockchain itself is secure, other components, such as wallets and decentralized applications (dApps), may not be as robust. Users must be vigilant about storing their private keys securely and using reputable platforms to mitigate the risk of hacking or theft.
Additionally, the technology remains complex and may be daunting for average users unfamiliar with how blockchain works. The challenge of educating users and providing intuitive interfaces will be crucial to fostering widespread adoption.
Overall, while blockchain offers substantial benefits, it is vital for stakeholders to be aware of the associated risks and navigate them carefully.
3. How is decentralized finance (DeFi) changing the financial landscape?
Decentralized finance (DeFi) is fundamentally altering the way individuals access and interact with financial services. DeFi platforms leverage blockchain technology to provide a wide range of services, including lending, borrowing, trading, and asset management,—all without the involvement of traditional banks.
This shift democratizes access to financial services, particularly for those who have historically been unbanked or underbanked. With DeFi applications, users can trade assets and earn interest on their holdings without the limitations often imposed by traditional banks, such as credit checks or geographical barriers.
Moreover, DeFi promotes innovation by allowing developers to create and launch new financial products directly on blockchain networks. This fosters a competitive environment where traditional financial institutions must adapt to remain relevant. The rapid growth of DeFi has also sparked increased interest in regulatory frameworks, leading to discussions on how to balance innovation with consumer protection.
In essence, DeFi is catalyzing a paradigm shift towards more accessible and innovative financial services, challenging the status quo of traditional banking.
4. What role do smart contracts play in blockchain finance?
Smart contracts are crucial components of blockchain finance, enabling automated and secure execution of financial agreements without the need for intermediaries. A smart contract is essentially a self-executing contract where the terms and conditions are written directly into code on the blockchain.
Smart contracts reduce counterparty risk, as they automatically execute when predefined conditions are met. For instance, in a loan agreement, a smart contract can trigger payment releases as the borrower meets specific milestones, ensuring compliance without manual oversight. This level of automation not only enhances efficiency but also minimizes potential disputes between parties.
Additionally, smart contracts can facilitate complex financial instruments such as derivatives and insurance, paving the way for innovative financial products that are more accessible and transparent. By employing smart contracts, stakeholders can enjoy streamlined processes, reduced costs, and increased trust in transactions.
In summary, smart contracts are transforming the financial landscape by providing secure, efficient, and automated solutions that can redefine how agreements are structured and executed.
5. How can blockchain finance enhance financial inclusion?
Blockchain finance has the potential to significantly enhance financial inclusion by providing access to financial services for underserved populations worldwide. Traditional banking systems often exclude individuals without access to physical banks or those who lack proper identification. However, blockchain technology can bridge these gaps.
Blockchain networks allow users to create digital identities and access financial services using only a smartphone and internet connection. This accessibility is particularly transformative for those in rural areas or developing countries, where banking infrastructure may be lacking. Moreover, blockchain's low transaction costs and absence of intermediaries can lower the barrier to entry for individuals who may not have the means to engage with traditional financial institutions.
Furthermore, the simplicity and transparency of blockchain transactions promote trust among users, encouraging them to engage with financial products they may have avoided due to skepticism about traditional banks.
As blockchain technology continues to evolve, its role in enhancing financial inclusion will likely grow, fostering greater economic opportunities and empowering individuals across the globe.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing the finance sector in profound ways, providing unprecedented opportunities that challenge the traditional banking model. While there are challenges that need to be addressed, the potential for enhanced security, reduced costs, and improved access to financial services is clear. As the fintech landscape continues to evolve, the lessons learned from the integration of blockchain in finance will shape the future of how individuals and businesses engage with financial products and services.
In this new frontier, understanding the intricacies of blockchain finance will be crucial for stakeholders looking to navigate the evolving landscape and capitalize on the opportunities it presents. The intersection of blockchain and finance is not just a trend; it is a transformative movement that is here to stay.